Cast magnesium alloy series : Characteristics and Uses of ZA41M Magnesium Alloy
AZ41M belongs to the Mg-Al-Zn alloy series. Its core advantages lie in "light and strong" (high specific strength), "quiet and stable" (noise reduction and vibration damping, stable size), and "multi-functional" (applied in heat dissipation, electromagnetic shielding, biocompatibility, etc.).
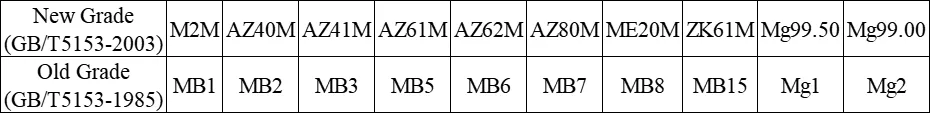
Comparison Table of New and Old Grades of Magnesium Alloys in China
I. Chemical Composition of AZ41M
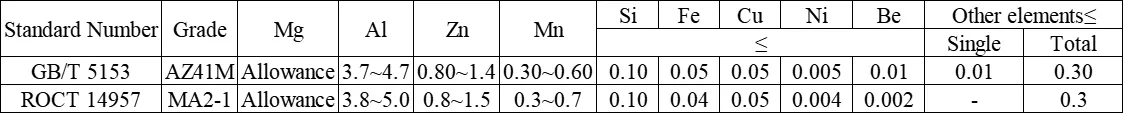
II. Mechanical Properties of AZ41M
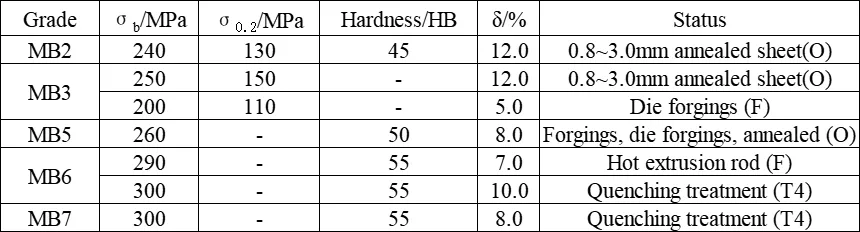
Mechanical Properties Comparison of Deformed Magnesium Alloys in the Mg-Al-Zn Series
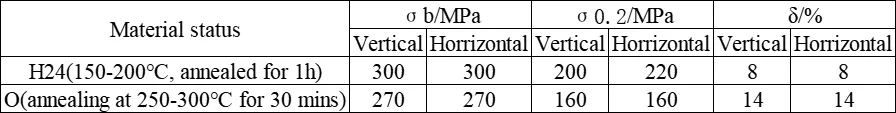
Mechanical properties at room temperature of AZ41M alloy sheet (sheet thickness: 0.8 - 3.0 mm)
III. AZ41M Application
In Mg-Al-Zn alloys, the alloying degree of MB2 and MB3 is the lowest. The Al content is no more than 5.0%, and it cannot be heat-treated for strengthening. Although the strength is somewhat lower, the process plasticity is better, making it suitable for processing various semi-finished products such as plates, rods, and forgings. Moreover, the SCC tendency is relatively low. The core applications of AZ41M focus on five civilian fields: environmental protection, consumer electronics, healthcare, energy, and transportation:
Industrial environmental protection equipment: used in wet flue gas desulfurization systems of coal-fired power plants, including flue gas baffle doors, flue lining, and components inside the absorption tower, relying on its corrosion resistance and dimensional stability to adapt to acidic environments and reduce equipment maintenance costs.
Consumer electronic products: as materials for mobile phones, computer casings, and heat dissipation components, it offers lightweight (density of only 1.82 g/cm³), electromagnetic shielding (shielding efficiency of 90 dB or more in the 30-200 MHz frequency band), and efficient heat dissipation advantages, enhancing product safety and portability.
Medical and household appliances: applied in surgical tool shells, rehabilitation device supports, etc., relying on biocompatibility and shock absorption and noise reduction properties; also used as magnesium rods for water heaters (sacrificial anode protection for the inner tank) and outdoor rescue fire starters to ensure the safety of civilian equipment.
New energy and energy storage: exploring as negative electrode materials for magnesium-air batteries, providing high energy density, supporting emergency power supply and other civilian energy storage scenarios, without involving sensitive military applications.
Lightweight transportation: replacing traditional metals in automotive steering components, bicycle frames, etc., through weight reduction to achieve energy conservation and consumption reduction, in line with the low-carbon policy orientation.

 EN
EN NL
NL FR
FR DE
DE JA
JA KO
KO PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES TR
TR